NEGATIVE EFFICACY RE-CONFIRMED
The vaccinated are more vulnerable to COVID: When it was known and who knew it
The most heavily vaccinated countries went on to have the most COVID
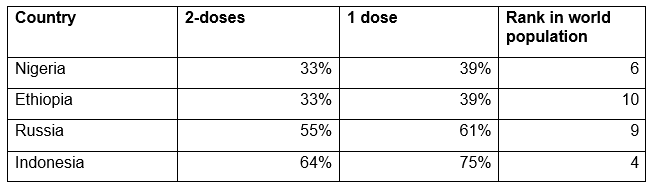
In March of 2023, the New York Times reported the percent uptake of COVID vaccines for each country. [1] Of the world’s ten largest countries, the most heavily COVID-vaccinated, as percent of their respective populations, were as follows, which I list below, along with the population rank of each: [2]
And the least COVID-vaccinated of the ten largest countries were:
Now let’s look at how those countries fared with regard with regard to reported COVID-19 cases following COVID vaccine rollout. The University of Oxford’s database, Our World In Data, shows that well after the COVID vaccine rollouts, the highest rates of COVID cases occurred in China, the most heavily vaccinated large country, and in the U.S. the third most heavily vaccinated (of at least one dose per person) of the ten largest countries. [3]
China and the U.S. are such extreme outliers, however, that we can better appreciate differences among the other six countries if for the moment we remove China and the U.S.
Now we can see that Nigeria and Ethiopia, followed by Indonesia and India, had the lowest rates of COVID cases of the 10 largest countries. The reader can verify this by following the link https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus/country/united-states to this interactive page, and hovering over each country. The highest case rates in the largest ten countries were in China, the United States, Russia and Brazil, which were overall more heavily vaccinated than the countries with the lowest case rates, as I will show further below.
For all eight of the above countries, the following graph, of cumulative COVID cases, shows that the COVID case rates worsened after rollout of the COVID vaccines in December 2020, and after 2021, the year of peak vaccine uptake. The heavily vaccinated countries then went on to have higher COVID-positive rates than the lesser-vaccinating countries. Let’s now quantify this disparity, by looking at cumulative case rates in the eight large countries noted above, showing both before and after the December 2020 vaccine rollout, as shown in Our World in Data. [4]
Readers will observe from the above graph that the enormous surge in cases occurred mostly after the December 2020 vaccine rollout, and continued strongly after world uptake of the COVID vaccines declined precipitously in 2022.
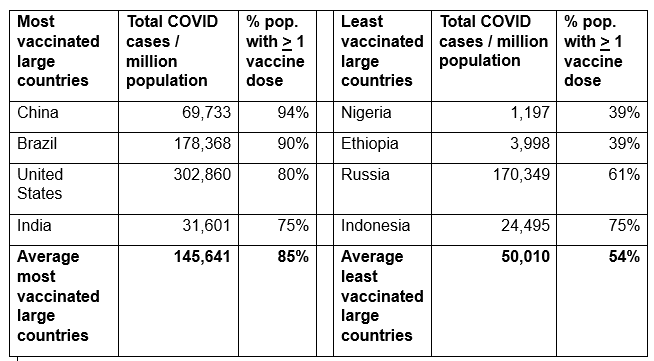
We see from the above graph that the four most heavily vaccinated large countries, China, the U.S., Brazil and India generally had more cumulative confirmed COVID case rates than the four least vaccinated large countries, namely Nigeria, Ethiopia, Russia and Indonesia.
Putting numbers to this, Our World In Data’s interactive graph shows the following total COVID cases, and I have listed next to those the percentage population receiving at least one COVID vaccine dose, from the table at the beginning of this article.
So an individual living in a heavily vaccinated large country had nearly triple the risk (=145,641 / 50,010) of having COVID disease of an individual living in a least vaccinated large country, while being 57% (= 85% / 54%) more likely to have received at least one COVID vaccine.
This is proof that the COVID vaccines did nothing to reduce transmission or to lower overall case rates. This fact alone should remove the COVID vaccines from the market.
The negative efficacy of the COVID vaccines shown here is not a surprising fact, because despite the vaccine industry’s position as the most heavily marketed and propagandized industry, or as some of us consider it, a religion, in world history, disease repeatedly follows in the wake of vaccines that are named for those diseases, including other respiratory diseases, such as the following:
There was more smallpox following the smallpox shot, [5] [6] more pertussis following the pertussis shot, [7] [8] more flu following the flu vaccine, [9] [10] etc.
It’s not only that vaccines against respiratory pathogens have never worked, and have never been broadly protective of the population, which even Anthony Fauci has admitted. [11] Nor can they work, due to the compartment problem that I describe below. Rather, the problem is that the vaccines’ negative efficacy subjects the vaccinated person to increased vulnerability to infection by the very agent that they fear, the pathogen for whom the vaccine was named. I will discuss the reasons for negative efficacy, and its mechanisms in the last two sections of this article.
No decrease in COVID deaths, no decrease in COVID hospitalization post-vaccine
COVID vaccine advocates have claimed that COVID cases in the vaccinated have been more mild, less risky for hospitalization and death than in the unvaccinated. However, this claim has been shown to be false. In fact, hospitalized COVID patients who were vaccinated were nearly twice as likely to die than unvaccinated COVID patients (70% versus 37%). [12] Also, the COVID vaccines did not reduce risk of hospitalization, as found in data analyst Steve Kirsch’s analysis [13] of this JAMA paper on VA hospital data. [14]
Revisiting the Cleveland Clinic Study
Cleveland Clinic’s now iconic graph below shows the COVID positivity results of their > 51,000 employees’ COVID results plotted against the number of COVID vaccine doses that each had received. [15] The black curve at the bottom shows COVID cases in unvaccinated employees, and the gold color curve at the top are the COVID cases in employees who received greater than three doses, with the other curves falling in between (1, 2 or 3 vaccine doses). Negative efficacy is not only confirmed, but is here shown to be dose-dependent.
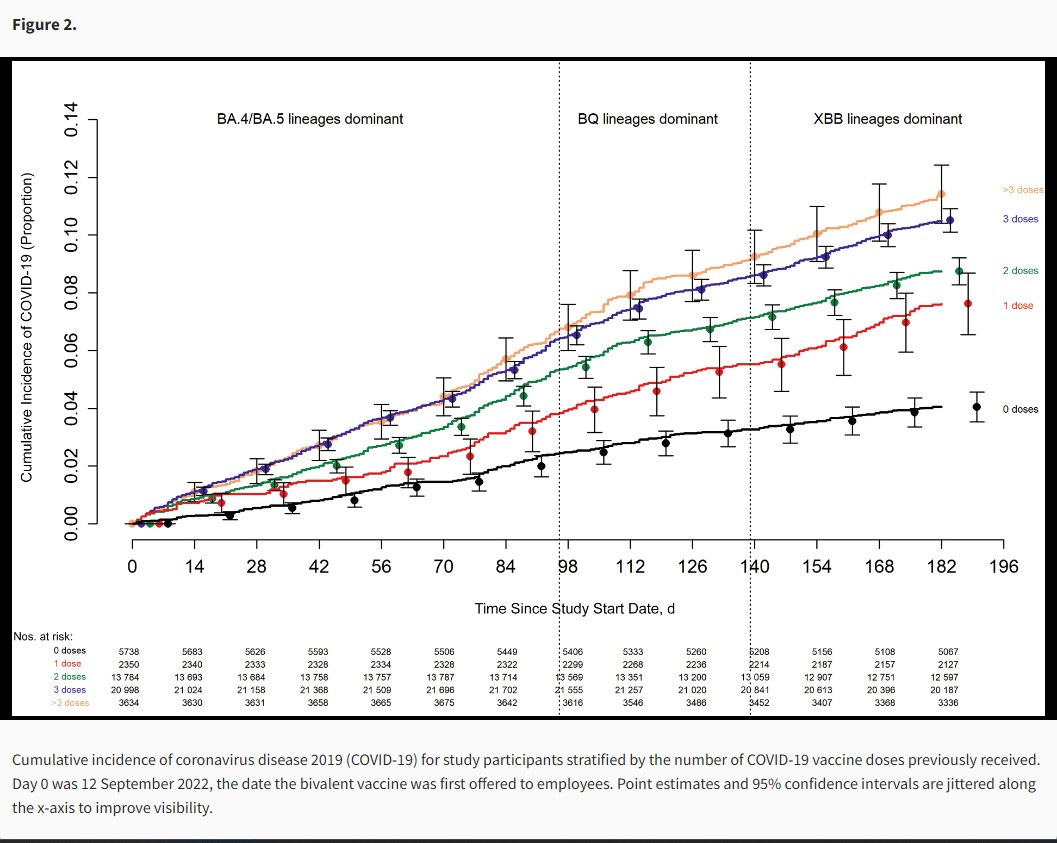
Then the difference persisted into 2023. No matter how many vaccine doses their “boosted-up-to-date” employees received, COVID-vaccinated employees still had more COVID-positivity than unvaccinated employees. [16] Notable is that in both graphs, from about 70 days on, even most of the margin of error bars do not overlap between the two cohorts, and, as with the earlier study, they continue to widen, each of which shows statistical significance of the findings, as seen below.

A Japanese study shows consistent findings with Cleveland Clinic
A December 2023 survey of small and medium size enterprise employees in Japan showed similar results to the Cleveland Clinic study: the more COVID vaccine doses, the more subsequent COVID infections. The results were published in December 2024. [17]
Although that paper begins with the usual silly praises of Pfizer and Moderna vaccines’ “high efficacy in preventing symptomatic infection,” the results undermine this claim in showing a positive correlation between COVID vaccine doses and COVID infections. The Cleveland Clinic study had similar false praise for the effectiveness of the mRNA vaccines in its opening paragraph, “The vaccines were amazingly effective . . .,” while the given data irrefutably undermined that claim.
Santa Clara County also confirmed negative efficacy
The data from a heavily vaccinated county in California supports the global findings of negative efficacy. Steve Kirsch studied the data released by Santa Clara County following his public records request. Santa Clara’s data showed that of COVID cases, 98% were previously vaccinated for COVID. However, the vaccination rate in that county was only 86%. [18]
The County’s Excel table can be downloaded here, and the reader can verify the County’s data: https://www.skirsch.com/covid/SCC_COVID_infections_Jan_2022.xlsx
From Santa Clara County’s tables of their cases of COVID, notice the percentage vaccinated over all age ranges in the bottom right corner.

Conversely, this also means that of the County’s positive COVID cases, only 2% were unvaccinated. Yet 14% of the County’s population remained unvaccinated.
Kirsch’s question is then: How do you have a greater likelihood of getting a disease that you were vaccinated for, unless the vaccine itself creates a problem?
The name of that problem is negative efficacy.
Was the FDA aware of the negative efficacy of the COVID vaccines?
By September 2021, the FDA and Pfizer were both aware that double-vaccinated people were more likely to test positive for COVID than the placebo/dose 2 group. That latter category is the cohort that, up to that point, had only received placebo, not vaccine, as a first dose. In fact, the Pfizer-double-vaccinated people tested positive for COVID at 70.3 cases per 1,000 person-years versus the 51.6 cases per person-years in those who had only had the second dose. This is a 36% (= 70.3 / 51.6) case rate increase of double-vaccinated over single vaccinated. The FDA’s admission of this fact is here: [19]

That fact is further evidence of the dose-dependent negative efficacy of the COVID vaccines, which is one of the most important of the Bradford Hill criteria to establish causation. So the FDA and Pfizer were both aware that you were more likely to test positive for COVID (36% more likely) if you had two COVID vaccines rather than only one. And they knew it by September 2021.
Was the CDC aware of the negative efficacy of the COVID vaccines?
The CDC recently published that, for children who had never tested positive for COVID, the Pfizer vaccine made children 2.59 times more likely to then test positive for COVID than unvaccinated children. “ . . . naïve participants vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech were more likely to be infected and experience symptomatic COVID-19 compared to naïve and unvaccinated participants (HR:2.59 [95% CI: 1.27-5.28]) . . “ [20] Unfortunately, this article is paywalled.
What is the mechanism of negative efficacy?
It has always been a quixotic attempt to fortify the body against respiratory viruses by means of injection outside the respiratory system, and it cannot possibly work. It is in essence a compartment problem. That is, respiratory pathogens must be fought and conquered in the venues of the nasal mucosa, nasopharynx and oropharynx, trachea and – if necessary – at the inner sanctum of the lungs, but definitely not in the irrelevant venue of muscle, lymph and blood, none of which normally enter the respiratory system, except in case of severe blunt force trauma.
The role of IgA
With regard to the COVID vaccines in particular, the antibodies that would be most useful in the respiratory compartment are the secretary immunoglobulins type A (IgA), and these are located at the mucosal surfaces, such as in saliva, that first confront viruses and other airborne pathogens before the rest of the body encounters them. IgA has shown strong effect against SARS-CoV-2 virus, effectively neutralizing the virus in vitro. And this was known by early December 2020, prior to the release of the COVID vaccines. [21] In fact, it was known by June 2020, that among antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2, the IgA were overwhelmingly dominant in earliest response to the virus. [22] In practical terms for a vaccine, this means that before the vaccine was even released to the public, it was already known that it was basically targeting the wrong compartment of the body, being released to muscle, flowing into blood and lymph but not into the respiratory compartment, where it would be most useful against this respiratory virus.
IgA, often called secretory IgA because of its function at the secretions from bodily surfaces, is essential for the defense against pathogens at the front lines of battle. That is, the body’s mucosal surfaces. This consists of preventing attachment to epithelial cells and by preventing viral reproduction by way of transcription, and by directly inactivating viruses. This was earlier observed regarding IgA’s role in influenza virus neutralization. [23] [24]
IgA is among the first of the immune cells to confront the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and it does a magnificent job at the front lines. IgA’s rejection and repulsion of viral invasion of the body is so effective that, as Mazanec et al write: “ . . . IgA could effectively eliminate from the body foreign substances which have penetrated the mucosa via an IgA-mediated transport shuttle back through the epithelium.”
One of the many tragedies of the COVID vaccines, however, is that they actually decrease the IgA antibodies. In fact, a study in Nature found that following vaccination, “IgA levels were significantly lower,” [with respect to naturally acquired COVID-19 infection] as shown below. [25]

The importance of robust IgA in defeating infection is shown in the results of the vaccinated participants of that study. The authors found: “Participants who experience a breakthrough infection have lower levels of vaccination-induced anti-Spike IgA.”
So people who needed IgA to repel SARS-CoV-2 were deprived of that protection from vaccinating, which left them more vulnerable to the infection. How ironic and tragic it was that the people most fearful of COVID illness submitted to injections that actually made them more vulnerable to that very same infection and disease.
[1] J Holder. Tracking coronavirus vaccinations around the world. Mar 13 2023. New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/world/covid-vaccinations-tracker.html
[2] Rank by Worldometers. https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/population-by-country/
[3] Our World In Data. Daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people. Jan 14 2025 update. https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus/country/united-states https://ourworldindata.org/covid-cases
[4] Our World In Data. Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people. Jan 14 2020 update. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-cases
[5] W Tebb. A Century of Vaccination and What It Teaches. Swan Sonnenschein & Co., London, 1898. pp. 93-94.
[6] J Hodge. Prophylaxis to be realized through the attainment of health, not by the propagation of disease. The St. Louis Medical & Surgical Journal. Vol 83. Jul 1902. p. 15
[7] F Mooi, N Van der Maas, et al. Pertussis resurgence : waning immunity and pathogen adaptation – two sides of the same coin. Feb 13 2013. Epidemiol Infect. 142 (4). 685-694. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9151166/
[8] A Schmidtke, K Boney, et al. Population diversity among Bordetella pertussis isolates, United States, 1935-2009. Aug 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 18 (8). 1248-1255. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3414039/
[9] D Skowronski, G De Serres, et al. Association between the 2008-09 seasonal influenza vaccine and pandemic H1N1 illness during spring-summer 2009: Four observational studies from Canada. Apr 6 2010. PLOS Medicine. https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1000258
[10] N Crum-Cianflone, P Blair, et al. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics of an outbreak of novel H1N1 (swine origin) influenza A virus among United States military beneficiaries. Dec 15 2009. Clin Infect Dis. 49 (12). 1801-1810. https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-abstract/49/12/1801/436062
[11] D Morens, J Taubenberger, A Fauci. Rethinking next-generation vaccines for coronaviruses, influenzaviruses, and other respiratory viruses. Jan 11 2023. Cell Host Microbe. 31 (1). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9832587/
[12] B Adhikari, J Bednash, et al. Brief research report: impact of vaccination on antibody responses and mortality from severe COVID-19. Oct 20 2023. Front. Immunol. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1325243/full#supplementary-material
[13] S Kirsch. VA data shows the flu and COVID shots don’t reduce your risk of hospitalization. Oct 22 2024. Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter.
[14] Y Xie, T Choi, et al. Risk of death in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 vs seasonal influenza in fall-winter 2022-2023. Apr 6 2023. JAMA. 329 (19). 1697-1699. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2803749#google_vignette
[15] N Shrestha, P Burke, et al. Effectiveness of the coronavirus disease 2019 bivalent vaccine. Apr 19 2023. Oxford Open Forum Infectious Diseases. https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/10/6/ofad209/7131292
[16] N Shrestha, P Burke, et al. Risk of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among those up-to-date and not up-to-date on COVID-19 vaccination by CDC criteria. Nov 8 2023. PLOS One. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293449
[17] E Nakatani, H Morioka, et al. Behavioral and health outcomes of mRNA COVID vaccination: A case control study in Japanese small and medium size enterprises. Dec 13 2024. Cureus. https://www.cureus.com/articles/313843-behavioral-and-health-outcomes-of-mrna-covid-19-vaccination-a-case-control-study-in-japanese-small-and-medium-sized-enterprises#!/
[18] S Kirsch. Whoops! FOIA response from Santa Clara County reveals that the COVID shots increased your risk of getting COVID. Mar 25 2024. Substack.
[19] FDA. FDA briefing document: Application for licensure of a booster dose for Comirnaty (COVID-19 vaccine, mRNA). Sep 17 2021. VRBPAC Committee Meeting. https://www.fda.gov/media/152176/download p. 22.
[20] L Feldstein, J Ruffin, et al. Protection from COVID-19 vaccination and prior SARS-CoV-2 infection among children aged 6 months – 4 years, United States, September 2022-April 2023. Dec 5 2024. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39656907/
[21] Z Wang, J Lorenzi, et al. Enhanced SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by dimeric IgA. Dec 7 2020. Sci Transl Med. 13 (577) https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7857415/
[22] D Sterlin, A Mathian, et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Jun 11 2020. Sci Transl Med. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abd2223
[23] M Mazanec, C Coudret, et al. Intracellular neutralization of influenza virus by immunoglobulin A anti-hemagglutinin monoclonal antibodies. Jun 10 1994. J Virology. 69 (2). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/instance/188717/pdf/691339.pdf
[24] S Armstrong, N Dimmock. Neutralization of influenza virus by low concentrations of hemagglutinin-specific polymeric immunoglobulin A inhibits viral fusion activity, but activation of the viral ribonucleoprotein is also inhibited. Jun 1992. J Virology. 66. 3823-3832. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC241168/?page=8
[25] S Sheikh-Mohamed, B Isho, et al. Systemic and mucosal IgA responses are variably induced in response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination and are associated with protection against subsequent infection. Apr 25 2022. Mucosal Immunol. 15. 799-808. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41385-022-00511-0









No vaccine has ever worked. Vaccines are one big hoax, a fraud.
Like I said in March 2020, I don't know what is going on, but I am sure they want us to be scared to death of it.
The dis ease is Fear. Fear is the disease, pray to God to be fearless in the face of viruganda...