STATIN DRUGS laid the groundwork for COVID
The best-selling class of drugs of all time took cholesterol to dangerously low levels, which deprived the immune system of its most essential molecule, vitamin D.
The following diagram shows the biochemical reaction that statin drugs stop.
It is the same reaction that initiates the cascade of events that build our strongest defense against viral infections.

Americans were sitting ducks.
I will argue in this paper that the massive population-wide lowering of cholesterol among the American public leading up to 2019 set the stage for vulnerability to the novel pathogen COVID-19, and that this weakening of people’s defenses turned what could have, and should have, been a nuisance common cold into a very difficult and dangerous illness for those who were already elderly, obese and / or who suffered from multiple chronic illnesses.
Statin drugs lower cholesterol, especially what is called “bad” LDL cholesterol. These drugs are among the most common prescriptions in the U.S. for decades. In 2014, the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association recommended that nearly everyone between the ages of 65 and 75 be prescribed a statin drug. [1] Then, by 2019, statins were a $10 billion dollar market, and over 92 million people in the US, mostly older adults, were taking statin drugs, [2] [3] which was 35% of the US population. This number was a three-fold increase over a decade earlier. [4] By 2020, the U.S. ranked 6th in the world in per capita statin use. [5]
So in 2019, the American public was about as saturated with statins as we had ever been.
The perhaps unintended result was that statin saturation rendered lots of seniors vulnerable to devastating outcomes from an infectious illness such as COVID, and that cumulative vulnerability, which peaked in 2019, likely represented the lowest point of collective immune capability, and those extremes crested right before COVID hit, as I will show in this paper.
Statin drugs lower a person’s cholesterol. And cholesterol – as shown in the diagram at the top – is not a luxury, but rather a necessity for forming the vitamin D molecule, which is the conductor of the symphony, so to speak, of the human immune system.
Here is another view [6] of the only path by which you can form vitamin D from sunlight. That path begins with cholesterol. (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol), at the bottom of the diagram, is fully activated vitamin D, ready to begin the synergistic coordinated actions of immune components against invasion by pathogenic viruses or other microbes.)

Notice in the figure above that three organs are involved in your vitamin D production: first the skin, then the liver, and finally the kidneys. This is to take vitamin D to where it’s fully activated for its role as the executive director of all of a person’s immune function, as in the diagram below.
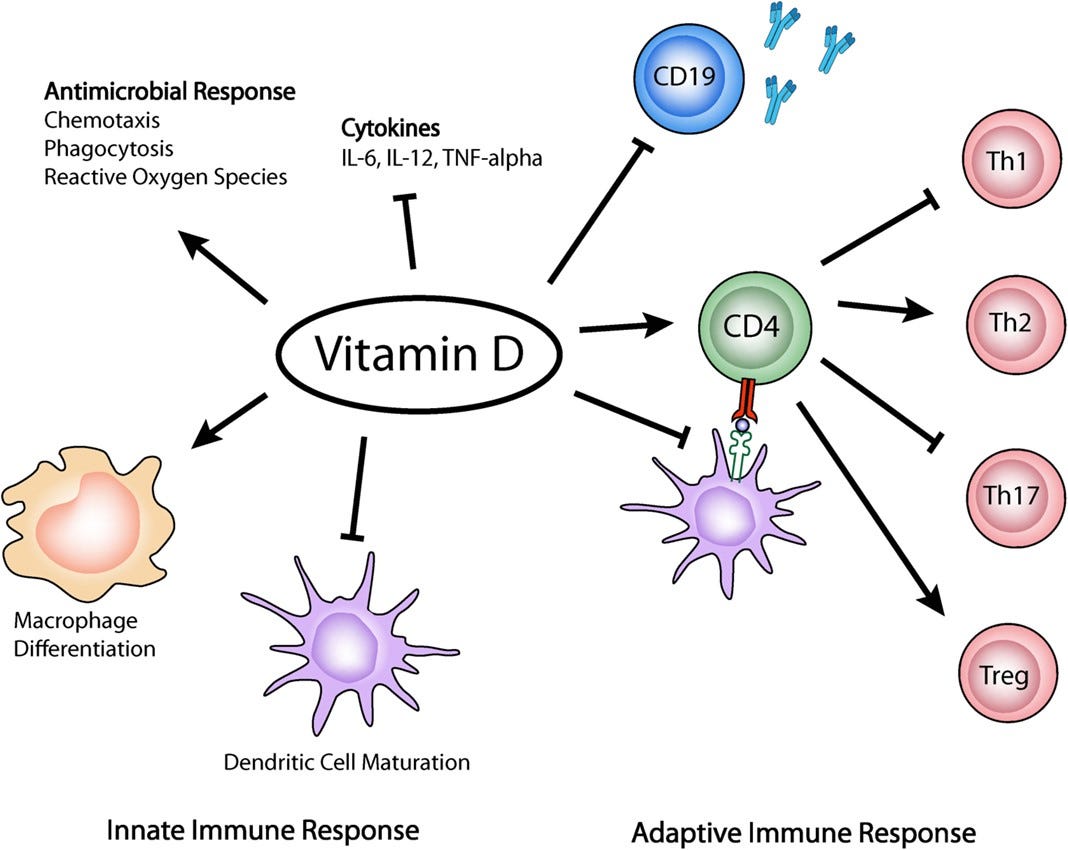
Vitamin D is the gateway nutrient to the proper functioning of the rest of the immune system, and was especially crucial in battling COVID, as I showed in over 130 study references to vitamin D’s role against COVID and other infectious illnesses – in both treatment and prevention – in my 2021 book The Defeat Of COVID. [7] Both those with higher blood lab values of vitamin D and those who supplemented vitamin D vanquished COVID much more readily with respect to lower hospitalization and lower deaths, than those who avoided vitamin D or who were deficient in it. Hundreds of studies and meta-analyses have shown this to be the case: Vitamin D pre-emptively defeats COVID and other respiratory and viral illnesses, especially when dosed, or produced in the skin from sunlight, early and regularly. [8]
Here is a very simplified view [9] of the central role that vitamin D plays in immune function.
Setting the stage for COVID vulnerability
The average age of COVID death was 81, which was 2 to 3 years beyond the U.S. life expectancy at that time, [10] so COVID very disproportionately affected seniors, especially those with obesity, type 2 diabetes, smoking, and > 2 co-morbidities. [11]
COVID morbidity and mortality in the U.S. far exceeded worldwide numbers. The U.S. has 4% of the world’s population, but 33% of the world’s deaths from COVID. The U.S. also had by far the greatest number of COVID diagnosed cases of any country, over 103 million, followed by India, Germany, Brazil and Japan, at 44 million, 38 million, 37 million and 33 million cases respectively. The US had 1.1 million deaths attributed to COVID. [12]
Our World In Data shows the U.S. with more COVID deaths per capita than any country, nearly tied with the UK and Italy, as of March 2023. [13]
Deaths and morbidity from COVID were augmented due to the medical system’s ignorance and incompetence about cholesterol, which led over recent decades to proliferation of statin drug prescriptions. This may have been influenced by a human tendency among the prescribers to turn away from uncomfortably unprofitable lines of inquiry, such as: How can cholesterol be bad, when it has so many functions in the body? Upton Sinclair said, “It is difficult to get a man to understand something when his salary depends on not understanding it.” It was just too inconvenient to question the ‘cholesterol bad, statins good’ mantra, if you were in the medical field.
Therefore, it was so much easier to demonize a devil-molecule in the body, and to sell a drug to rid the vilified substance than to examine if the devil-molecule were a threat to health in the first place.
So then we need to ask: What does cholesterol do, and how does it work?
What does cholesterol do?
Cholesterol is essential to the life of every cell in the body. The liver makes it when we don’t get enough from food; the liver makes about 75% to 80% of our cholesterol, [14] [15] with the other 20% coming from food, which is one indication of how badly we need it.
The cholesterol carried by the LDL lipoprotein (so-called “bad cholesterol”) is particularly valuable, because it is the major vehicle by which cholesterol is carried to the cells. When cholesterol arrives there, it forms an essential component of cell membranes. For humans as well as other mammals – which includes those mammals who live on fries and chips, as well as those foraging among nature - cholesterol is such an important fat in mammalian cell membranes that it makes up about 30% of the lipid bi-layer. [16] Cholesterol is what keeps our cell membranes supple and strong, while enabling the essential signaling transduction that life requires. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging has shown that cholesterol is required for the essential flow of signaling proteins. [17] Without signaling among our cells, the body would have no means to enable continued life; conversely, one definition of death might be the end of that cooperative interaction among the cells of the body.
The neurons are cells that are even more dependent on cholesterol than most, and cholesterol is abundant throughout the central nervous system. The brain’s high level of cholesterol is necessary for the connections among neurons to function well. When cholesterol is lowered, damage to memory and cognition has been seen to follow. [18] in mice, [19] as well as in humans. [20] Lower cholesterol levels have also been correlated with violent behaviors. [21] Deficiency of cholesterol has been seen in Parkinson’s disease: “Higher cholesterol levels are associated with a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease. Higher LDL-cholesterol in Parkinson’s also has been linked to slower loss of motor and executive function.” [22] Observations of Framingham Heart Study participants showed “a significant positive linear association between total cholesterol and measures of verbal fluency, attention/concentration, abstract reasoning and a composite score measuring multiple cognitive domains.” [23]
Cholesterol is necessary to digest foods, as it is the main source material for bile acid production. [24] Bile acids facilitate absorption of nutrients, and they act as a detergent to break down fats, so they are the main way that the liver catabolizes dietary fats and cholesterol.
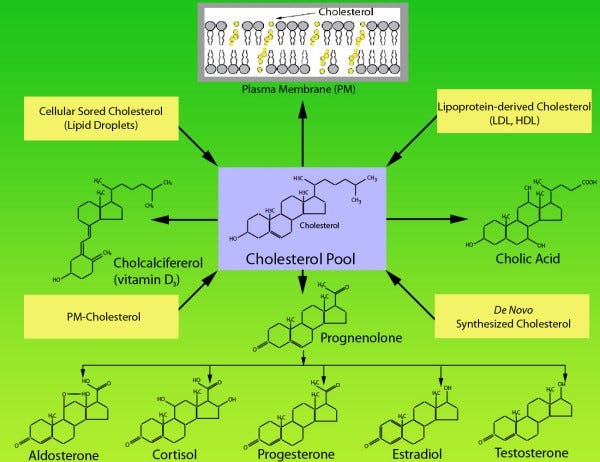
Cholesterol is the substrate for our reproductive hormones, testosterone, progesterone and estrogen, as well as our glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. This occurs in the gonads in youth, and in the adrenal glands throughout life. So cholesterol is required for adequate adrenal function.
And finally, and most pertinently to the topic of this paper, cholesterol is required for vitamin D synthesis, which is needed for life after COVID, as well as victory over other pathogenic microbes, as discussed above.
Hu and Zhang show all the major functions of cholesterol in this figure. [25]
How statin drugs work
Statin drugs target and inhibit, really they poison, our enzyme that is necessary to form cholesterol. The enzyme is HMG CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase) in the blood and the liver. Without this enzyme, we cannot produce cholesterol. Statins are especially effective at reducing LDL cholesterol, which has been called “bad cholesterol” so often and so ubiquitously that both doctors and patients have come to accept this as true. The trouble is that it’s not true that LDL is bad. Dr. Aseem Malhotra is the UK’s most widely recognized cardiologist. He says this about LDL cholesterol: “It’s a useless biomarker in terms of predicting someone’s risk of heart disease and therefore we shouldn’t obsess about lowering it.” [26] His book, A Statin Free Life, argues that statins are not at all adequate or appropriate for preventing heart disease.
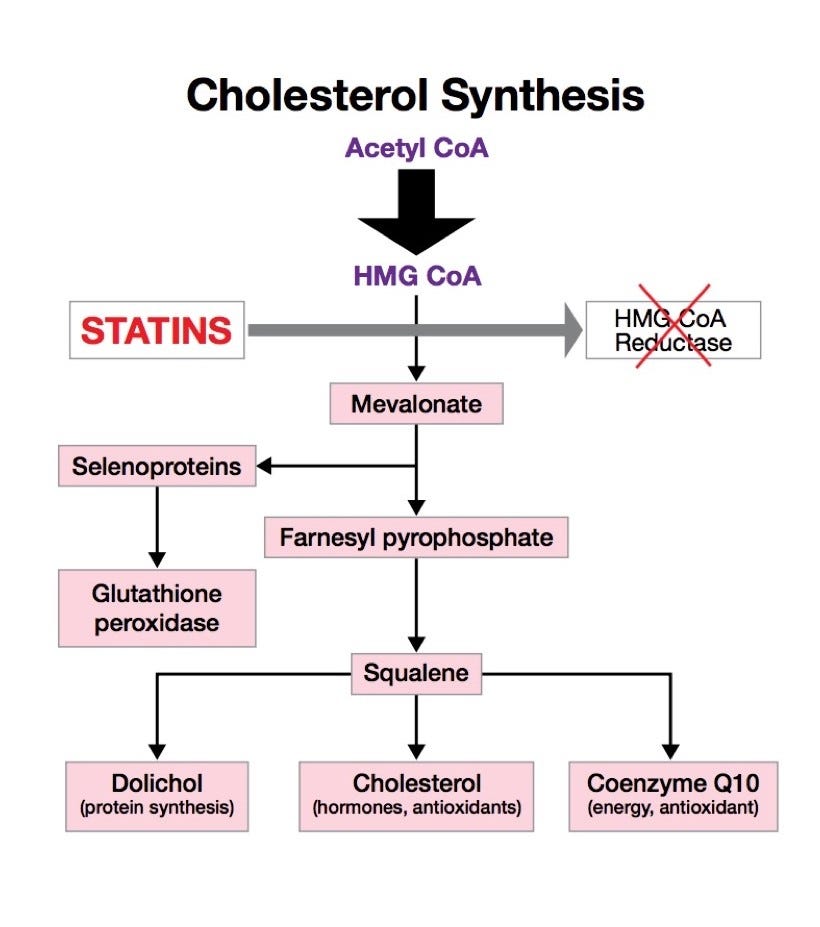
Poisoning is a strong word, and it should probably be used sparingly. The destructive effect of statin drugs on the enzyme HMG CoA reductase not only has the effect of reducing production of cholesterol, especially LDL cholesterol, but also of coenzyme Q10, as can be seen in the upstream dam in the following diagram. [27] This in turn reduces flow to each of the downstream pathways.
The problem with reducing CoQ10 is that doing so impairs mitochondrial function, because CoQ10 is key to the electron transport chain, which is required for ATP production to keep the body alive. So CoQ10 and mitochondria generally are also necessary for life and thriving good health. The loss of CoQ10 from statin prescription is the most likely explanation for the frequent muscle pain and fatigue suffered by those taking statins. That is, when your low CoQ10 fails the needs of your mitochondria, then your mitochondria fail the needs of your muscles, including the heart, which is nearly all muscle. The Cochrane Heart Group writes: “The severity of heart failure correlates with the severity of coenzyme Q10 deficiency.” [28] You see, when you attempt to selectively poison one biochemical pathway, such as the cholesterol-forming pathway, you end up with rather nasty unintended consequences from damage to the various parallel tributaries downstream.
The resulting damage was not lost on the people taking statin drugs, and so when inevitable side effects accumulated, compliance with prescriptions turned out to be low. Statins are such a hard to tolerate class of drugs that 75% of people who were prescribed statins were no longer taking them a year later. [29]
Everything you were told about statin drugs and cholesterol was wrong.
”The four-decade global campaign to curb heart disease by lowering cholesterol through diet and drugs has sadly failed.” [30] -- Dr. Aseem Malhotra, Cardiologist
A reader who is at all familiar with my previous articles or books knows that to describe me as a medical contrarian is an understatement. Case in point, my total cholesterol, last time measured, was 289, and that is where I want it, especially now in my senior years, due to extensive, not deficient, study of cholesterol’s vital roles in the body.
However, most conventional medical providers are convinced that cholesterol is the body’s arch-enemy molecule, particularly the feared LDL and VLDL, for being the alleged couriers of heart disease. Even while admitting that only one in eight randomized trials of statins’ effect on mortality showed decreased all-cause mortality, [31] the American Medical Association, the American Heart Association, and all other mainstream medical organizations repeat and reinforce the belief among themselves, as well as to the believers among the rest of the medical profession, the media and the public, that cholesterol is a problem molecule, and their job is to reduce it.
Researchers Byrne and Demasi did a systematic review and meta-analysis of 21 statin trials involving over 140,000 subjects. They found “no consistent relationship between lowering LDL-C and death, heart attack or stroke, following statin therapy.” [32]
Before the COVID vaccines, and their abysmal efficacy and hazards, statin drugs had the worst benefit to risk ratio of any class of drugs. Even when viewed in the most favorable light possible, even among studies that were already biased pro-statin, it was found that over five years, statins could at best offer 3 to 4 additional days of life. [33] That’s it, in the most favorable possibly circumstances: 3 or 4 days more over a five-year period.
Statin makers have never made their data available to the public, and regulators have helped them hide their data from outside observers. [34]
Clinicians have complained for many years about their patients’ reactions to statins. One writes: “Ever since the statins hit the market, colleagues and I began observing case after case of individuals who lost sensation in their body, developed muscle pains, or had cognitive decline set in once they started the statin, which immediately resolved once they stopped the statin.” [35]
One study found significant decline in 3 of 5 measures of cognitive function in the statin-treated group compared to placebo. “Subjects with the lowest post-treatment LDL-cholesterol levels had the greatest decrements in function.” [36]
Statin drugs have also been correlated with an increase in diabetes. A 48 to 71% increase in new onset type 2 diabetes was observed with statin drugs. [37] [38]
Low cholesterol levels have also correlated with cancers, in this JAMA meta-analysis of over 360,000 men. “Mortality follow-up revealed a significant excess of cancer in the lowest decile of serum cholesterol level . . .” [39]
“Statins are the biggest fraud in modern medicine,” wrote David Brownstein MD in 2015. [40]
Are there nefarious political or financial interests at work?
No, I am not suggesting a conspiracy among the medical profession to make people vulnerable to illness, and then to hit them with the largest pandemic extravaganza psy-op production in history, which led to four trillion dollars finding their way upward to create hundreds of new billionaires, beginning with mass mask stifling and lockdowns strangling small businesses and communities, and ending with the toxic COVID vaccines, while instilling fear and obedience into all generations of the public. That might have happened with some planning, but I am not best qualified to know the intentions or behind-closed-doors activities of the powers that be.
The statin craze of our era has reduced people’s cholesterol, which in turn took away people’s ability to make vitamin D in the skin on sun exposure. (A possibly separate issue is that decades of propaganda against sunlight may be due to the fact that sunlight is free and has no shareholders, but there is money to be made from sales of sunscreens.) So now we have a population that had thrown away their cholesterol, and thereby impaired their ability to make vitamin D and were afraid of sun exposure.
If there is a conspiracy to be found there, I leave it to investigative journalists and political pundits to work that out, discerning the sly maneuvers of sneaky perpetrators. I have no talent in ferreting out corruption or conspiracies. Rather, I think we have witnessed a medical system that perpetuates its role in people’s lives by heavy-handed promotion of gateway drugs such as vaccines and statins. The 10+ story children’s hospitals in major cities have been built from the injuries caused by vaccines, and untold numbers of elderly are seen by their families to wither away into weakness and convalescence once statin drugs rob them of their strength.
Somehow, the general population had not only been convinced the human immune system was conferred by multiple injections in childhood, but that one’s own cholesterol was a sinister, dangerous substance. We are a drug-soaked culture. 66% of US adults take pharmaceuticals, [41] and half of US seniors take four or more prescription drugs. [42]
The statin drugs sit at the top of this heap, and although I mentioned earlier that the statin industry was worth $10 billion in 2019, it has been projected to rise to $1 trillion per year worldwide, even despite the expiration of their patents. [43] These figures do not take into account the sub-industry of drugs, nurtured by the statin gateway, that are prescribed for all the side effects caused by statins.
Humanity at a crossroads
The medical system’s nationwide, multi-decade statin saturation campaign was most likely done in the profit-seeking pursuit of pharma’s shareholders’ best financial interests. It would be naïve to deny such an influence over the medical industry.
Now the debate over whether cholesterol is too low or too high may be moot to some extent, if up to 78% of one’s cholesterol may be genetically determined. [44] Each of us derives our bodily features in great part from our parents and earlier ancestors, both in external appearance and internal strengths and vulnerabilities.
No matter what part of the world we hail from, our distant ancestors were no sloths. We are the rightful heirs to the perfect bodies that they bequeathed to us, at least through genetic blueprint, the bodies they used to endure all-day movement and work, throughout all extremes of heat and cold, whether there was a famine going on or not, who likely had to walk great distances to find food or even water. But our current generations have been drugged since birth with vaccines and other harmful substances and pollutants. So many of us have been cut down by those substances and we have not been able to fully enjoy that birthright of strong, agile, energetic bodies. Our ancestors were just fine with their cholesterol. The first heart attack was not described in the medical literature until the year 1910. [45] Angina pectoris was described in the 18th century. Was it that the ancient physicians Hippocrates, Maimonides, Paracelsus and their peers were too obtuse to see chronic disease all around them, as we are surrounded by among our contemporaries? Was it that they ignored or did not detect heart disease, which turned out to be the biggest killer of the last century in our time? Did they ignore every patient who said they felt “as if an elephant is sitting on my chest,” which is what a heart attack feels like? Or is it that their peers did not suffer from heart disease and the chronic disease that plague our families and friends?
With the debacle of the COVID vaccines and then the newfound awareness by the public that childhood vaccines and other pharmaceuticals have harmed people’s health, we may be able to turn around the slow poisoning of current generations and maybe even abandon that practice altogether in the future.
[1] M Miedema, F Lopez, et al. Eligibility for statin therapy according to new cholesterol guidelines and prevalent use of medication to lower lipid leves in an older US cohort. Jan 2015. JAMA. 175 (1). 138-140. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/1935930
[2] Cleveland Clinic. Statins. Mar 12 2024. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22282-statins
[3] L Yourman, I Cenzer, et al. Evaluation of time to benefit of statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events in adults aged 50 to 75 years: A meta-analysis. Nov 16 2020. JAMA. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2773065
[4] A Matyon, C Brown, et al. Statins utilization trends and expenditures in the U.S. before and after the implementation of the 2013 ACC / AHA guidelines. Jun 2023. 31 (6). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10203693/
[5] J Guadamuz, A Shooshtari, et al. Global, regional and national trends in statin utilization in high-income and low-middle-income countries, 2015-2020. Sep 8 2022. BMJ Open. 12 (9). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9462115/
[6] X Feng, J Ashley. Metabolic bone disease II, in Pathobiology of Human Disease. 2014. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/7-dehydrocholesterol-reductase
[7] C Huber. The Defeat of COVID. Apr 2021. https://www.amazon.com/Defeat-COVID-medical-studies-doesnt/dp/0578248212
[8] C19early.org. Vitamin D for COVID-19. Apr 2024. https://c19early.org/d
[9] M Iruretagoyena, D Hirigoyen, et al. Immune response modulation by vitamin D: role in systemic lupus erythematosus. Oct 11 2015. Frontiers Immunol. 6-2015. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00513/full
[10] C. Huber, B Borovoy. Data that disprove the COVID-19 pandemic. Dec 19 2020. PDMJ. https://pdmj.org/papers/is_there_a_pandemic
[11] I Djaharuddin, S Munawwarah, et al. Comorbidities and mortality in COVID-19 patients. Dec 17 2021. Gac Sanit. 35. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8677356/
[12] Coronavirus Resource Center. Mortality Analyses. Mar 10 2023. Johns Hopkins U Med. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/mortality
[13] Global Change Data Lab. Our World In Data: Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million people. https://ourworldindata.org/explorers/coronavirus-data-explorer
[14] R Kiss, A Sniderman. Shunts, channels and lipoprotein endosomal traffic: a new model of cholesterol homeostasis in the hepatocyte. 2017. J Biomed Res. 31 (2). 95-107. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5445212/
[15] The Cleveland Clinic. What is cholesterol? https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/23922-what-is-cholesterol
[16] J Zhang, Q Li, et al. Cholesterol content in cell membrane maintains surface levels of ErbB2 and confers a therapeutic vulnerability in ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Feb 20 2019. Cell Commun Signal. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6383291/
[17] G Jaipuria, T Ukmar-Godec, et al. Challenges and approaches to understand cholesterol-binding impact on membrane protein function: an NMR view. Mar 8 2018. Springer: Cell Mol Life Sci. 75. 2137-2151. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00018-018-2789-9
[18] M Muldoon, S Barger, et al. Effects of lovastatin on cognitive function and psychological well-being. Aug 16 2004. Am J Medicine. https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(00)00353-3/fulltext
[19] U Guo, G Zou, et al. Simvastatin impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognitive function in mice. Feb 24 2021. Mol Brain. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7905661/
[20] A Malhotra. A Statin Free Life. 2021. https://www.amazon.com/Statin-Free-Life-Dr-Aseem-Malhotra/dp/1529354102
[21] A Golomb. Cholesterol and violence: is there a connection? Mar 15 1998. Ann Intern Med. 128 (6). 478-487. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9499332/
[22] X Huang, N Sterling, et al. Brain cholesterol metabolism and Parkinson’s disease. Mar 2019. Mov Disord. 34 (3). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6420391/
[23] P Elias, M Elias, et al. Serum cholesterol and cognitive performance in the Framingham Heart Study. Jan-Feb 2005. Psychosom Med. 67 (1). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15673620/
[24] T Li, J Chiang. Regulation of bile acid and cholesterol metabolism by PPARs. Jul 14 2009. PPAR Res. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2712638/
[25] J Hu, Z Zhang, et al. Cellular cholesterol delivery, intracellular processing and utilization for biosynthesis of steroid hormones. Jun 1 2010. Nutr Metab. 7 (47). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2890697/
[26] K Grosser. Should you take statins? https://kentcardio.com/should-you-take-statins/
[27] R Lilly. Reaping the benefits of ubiquinol. Mar 12 2018. FX Medicine. https://www.fxmedicine.com.au/blog-post/reaping-benefits-ubiquinol
[28] T Al Saadi, Y Assaf, et al. Coenzyme Q10 for heart failure. Feb 3 2021. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 (2). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8092430/
[29] J Rogan. Dr. Aseem Malhotra MD. Joe Rogan Experience #1979. https://www.jrepodcast.com/episode/joe-rogan-experience-1979-dr-aseem-malhotra/
[30] A Malhotra. A Statin Free Life. 2021. https://www.amazon.com/Statin-Free-Life-Dr-Aseem-Malhotra/dp/1529354102
[31] L Yourman, I Cenzer, et al. Evaluation of time to benefit of statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events in adults aged 50 to 75 years: A meta-analysis. Nov 16 2020. JAMA. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2773065
[32] P Byrne, M Demasi, et al. Evaluating the association between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction and relative and absolute effects of statin treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mar 14 2022. JAMA Internal Med. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/article-abstract/2790055
[33] M Kristensen, P Christensen, et al. The effect of statins on average survival in randomization trials, an analysis of end point postponement. 2015. BMJ Open. https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/5/9/e007118.info
[34] BMJ. Statins – a call for transparent data. https://www.bmj.com/campaign/statins-open-data
[35] A Midwestern Doctor. What can statins teach us about the COVID-19 vaccines? May 4 2023.
[36] M Muldoon, S Barger, et al. Effects of lovastatin on cognitive function and psychological well-being. Aug 16 2004. Am J Medicine. https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(00)00353-3/fulltext
[37] A Culver, I Ockene, et al. Statin use and risk of diabetes mellitus in postmenopausal women in the women’s health initiative. Jan 23 2012. JAMA Internal Medicine. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/1108676
[38] B Hoogwerf. Statins may increase diabetes, but benefit still outweighs risk. Jan 2023. Cleveland Clinic J Med. 90 (1). 53-62. https://www.ccjm.org/content/90/1/53#ref-6
[39] R Sherwin, D Wentworth, et al. Serum cholesterol levels and cancer mortality in 361,662 men screened for the multiple risk factor intervention trial. Feb 20 1987. JAMA. 257 (7). 943-948. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/364558
[40] D Brownstein. The Statin Disaster. 2015. p. 28.
https://drbrownstein.com
[41] Health Policy Institute. Prescription Drugs. 2002. Georgetown University. https://hpi.georgetown.edu/rxdrugs/
[42] A Kirzinger, T Neuman, et al. Data note: Prescription drugs and older adults. Aug 9 2019. KFF. https://www.kff.org/affordable-care-act/issue-brief/data-note-prescription-drugs-and-older-adults/
[43] M Demasi. Statin wars: have we been misled about the evidence? A narrative review. Jul 2018. Br. J Sports med 52 (14). 905-909. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29353811/
[44] D Heller, U deFaire, et al. Genetic and environmental influences on serum lipid levels in twins. Apr 22 1993. N Engl J Med. 328 (16). 1150-1156. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199304223281603
[45] W Fye. The delayed diagnosis of myocardial infarction: it took half a century. Aug 1985. 72 (2). https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1161/01.CIR.72.2.262





Before statins a recommended total cholesterol level was 300. Once statins were available it dropped to 200...with no scientific support. This is why I say Doctors are glorified Drug Reps☠️
I have been ambivalent about statins for years. A couple of months ago Dr. McCullough, who I admire greatly, endorsed the use of statins in a general sense in one of his Substack articles. That persuaded me to continue my doctor's Lipitor prescription which I had stopped because of the chorus of experts like yourself who have been courageous enough, like Dr. McCullough, to present a contrarian view on medical issues. But your article demonstrates persuasively to a layman like me that statins harm the immune system and reduce the body's ability to make essential Vitamin D. I don't want to harm my immune system any more than I already have from all the toxins in processed food and all the toxins in the air and water and the modern electromagnetic environment and now the poisonous "vaccines" which I thankfully refused. I want to live more as God intended and I want to preserve the Eden that God provided. Until I can be persuaded otherwise, no more statins for me.